In addition to knit and woven fabrics, non-woven backing materials help to enhance the quality of artificial leather.
Non-woven fabric is a type of fabric that is created by bonding fibers together without weaving them. This creates a fabric that is lightweight and can be made stronger by increasing its thickness. Non-woven fabric is often used in the making of synthetic leather because it provides structure and support to the material.

Non-woven fabric is a common choice for backing material in the production of faux leather. This material is made by bonding fibers together mechanically, thermally, or chemically, rather than weaving or knitting them together.
Non-woven fabrics provide several benefits when used as backing materials for faux leather, including:
Absorbency: Non-woven fabrics can absorb moisture and other liquids, which can be helpful in the production process, especially for gluing the faux leather to other materials such as notebooks.
Strength and durability: Non-woven fabrics can be made thick and strong, providing a stable base for the faux leather.
Stability: The fibers in non-woven fabrics are randomly oriented, which provides stability and prevents stretching or distortion of the faux leather.
Flexibility: Non-woven fabrics are flexible and can conform to the shape of the faux leather.

1. The production
Non-woven fabric is typically made from a combination of three main types of materials:
- Natural fibers such as cotton, linen, and jute.
- Renewable fibers such as bamboo, viscose, Tencel, and modal.
- Synthetic polymers such as PP, PE, PET, nylon, PA, polyester, PCL, and PLA.
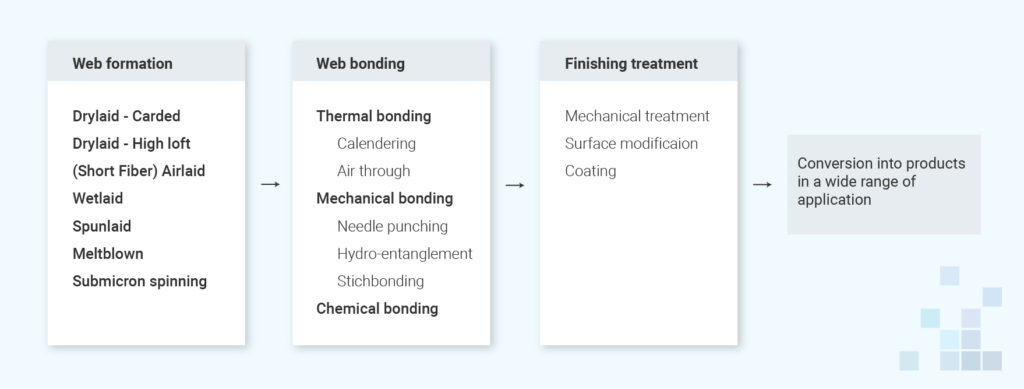
To produce non-woven fabric for use as backing material for faux leather, the raw materials are first cleaned, sorted, and carded to form a web. There are several methods for producing non-woven fabric, but a general process can be defined in three stages. Modern technology allows for some overlap of these stages, and in some cases, all three stages can occur simultaneously.
The three stages of producing non-woven fabric are:
- Web formation
- Web consolidation
- Finishing
During web formation, fibers are laid out to form a web. Web consolidation involves bonding the fibers together to form a cohesive fabric. Finishing is the final stage, and it involves treating the fabric to enhance its properties or appearance.
Stage 1: Web formation
Non-wovens manufacturing begins with arranging fibers into a sheet or web. These fibers can be either staple fibers or filaments extruded from molten polymer granules.
There are different methods to do web formation
- Drylaid – Carded
- Drylaid – High loft
- (Short Fiber) Airlaid
- Wetlaid
- Spunlaid
- Meltblown (phương pháp nấu chảy)
- Submicron spinning
Stage 2: Web bonding
Webs have limited initial strength right after formation, depending on various bonding mechanisms. Therefore, webs need to be consolidated in one way or another. The choice of web consolidation method strongly depends on the required functional properties and the type of fibers used.
There are three basic types of bonding:
- Thermal bonding (cohesive bonding)
- Mechanical bonding
- Chemical bonding (adhesion bonding)
Stage 3: Finishing treatment
The nonwoven industry produces a wide range of products thanks to the ability to combine different raw materials and technologies. Additionally, finishing treatments can tailor or functionalize nonwovens to meet specific properties, enhancing the industry’s diversity even further.
Finishing treatments can be either mechanical or chemical. Mechanical treatments such as stretching, perforating, and crimping can modify the nonwoven’s properties. Chemical treatments, on the other hand, modify the surface of the fibers to change the haptics or repellency of the nonwoven.
With finishing treatments, nonwovens can be made conductive, flame retardant, water repellent, porous, antistatic, breathable, absorbent, and much more. Nonwovens can also be coated, printed, flocked, dyed, or laminated to other materials.
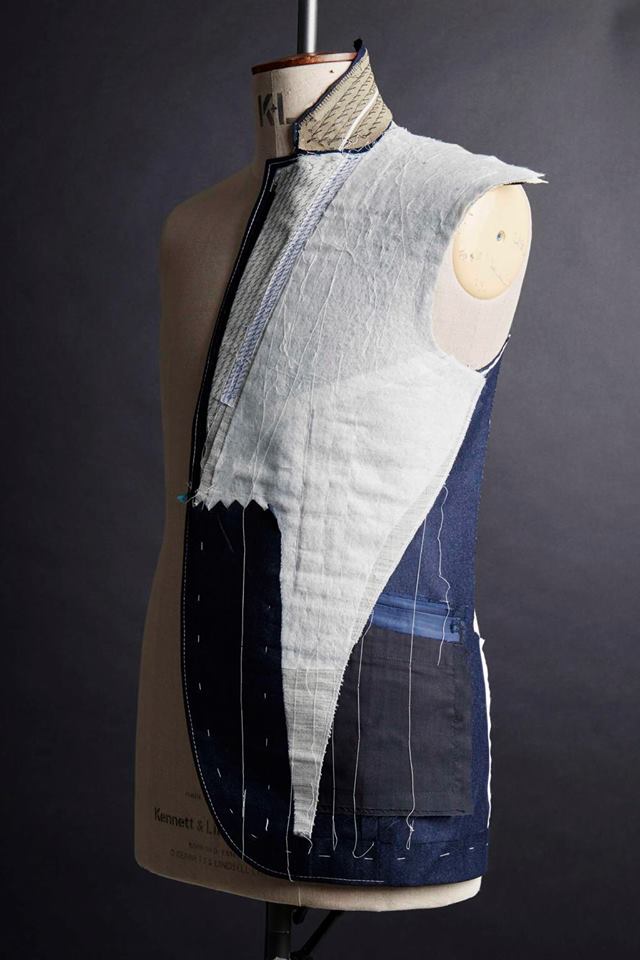
2. Non-woven fabric in the garment industry
Non-woven fabrics are widely used in the garment industry for different purposes. One of the most common applications of non-woven fabrics in the garment industry is as interlining or interfacing. Interlining is a layer of material that is added between the outer fabric and the lining of a garment to provide support, structure, and shape. Interfacing, on the other hand, is a layer of material that is added to specific areas of a garment to provide additional support and structure.
Non-woven fabrics are an excellent choice for interlining and interfacing because they are lightweight, flexible, and easy to work with. They provide stability and structure without adding bulk to the garment. Additionally, non-woven fabrics can be bonded to other fabrics using heat or adhesive to create a strong and durable bond.
Non-woven fabrics are also used in the production of disposable garments, such as medical gowns, surgical masks, and protective clothing. These garments are made using non-woven fabrics that are engineered to provide specific properties, such as barrier protection, breathability, and fluid resistance.
In addition to interlining, interfacing, and disposable garments, non-woven fabrics are used in the garment industry for other purposes, such as:
- Lining: Non-woven fabrics can be used as a lining material for jackets, coats, and other outerwear. They provide warmth and insulation without adding bulk to the garment.
- Padding: Non-woven fabrics can be used as a padding material for shoulder pads, sleeve heads, and other areas of a garment that require additional structure and support.
- Embroidery: Non-woven fabrics can be used as a stabilizer for machine embroidery. They provide stability and prevent the fabric from puckering or stretching during the embroidery process.

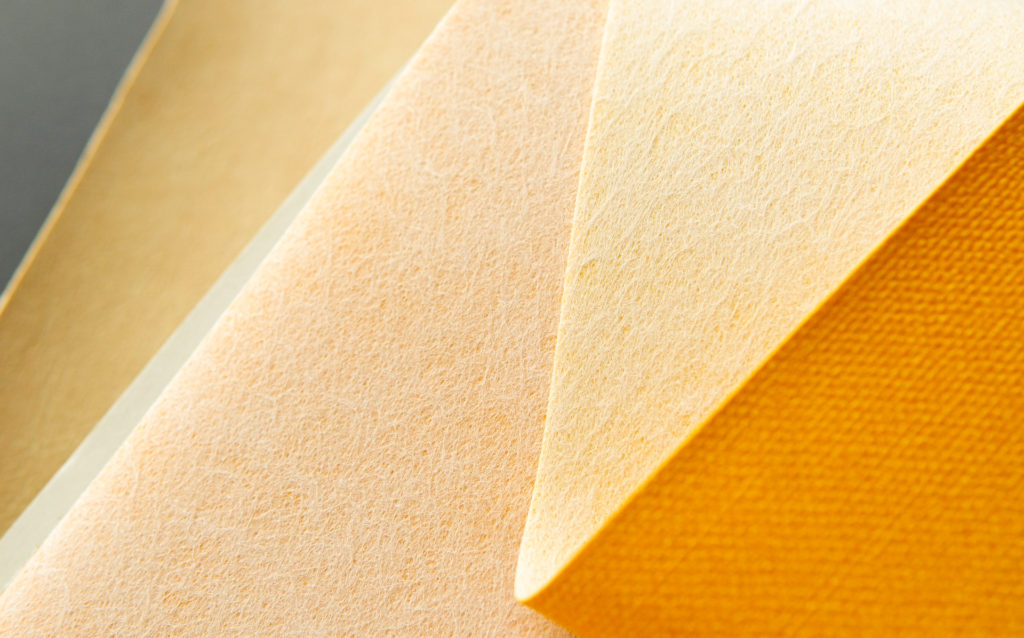
3. Non-woven fabric in the synthetic leather industry
Non-woven fabrics are a popular choice for backing fabric in artificial leather due to their ability to provide a strong and stable base for the material. This is important because artificial leather, made from materials such as polyurethane and PVC, requires a sturdy backing to give it structure and durability. Non-woven fabrics offer this stability without adding significant weight, making them ideal for this purpose.
Moreover, non-woven fabrics can be treated with various coatings and finishes to enhance their properties. These treatments can add features such as water repellency or increased resistance to abrasion, which further improves the durability and performance of the artificial leather material. This makes non-woven fabrics suitable for a wide range of applications.

Non-woven fabric is an essential material in the production of artificial leather. It provides absorbency, strength, and stability, and there are many types of non-woven fabrics that can be used depending on specific requirements. The production process for non-woven fabric may vary, but the result is a reliable and durable backing material that helps to create high-quality faux leather products. Non-woven fabrics are also widely used in the garment industry for interlining, interfacing, and other purposes. Overall, non-woven fabrics offer unique properties that make them an important component in the production of artificial leather and other materials.



Leave a Reply